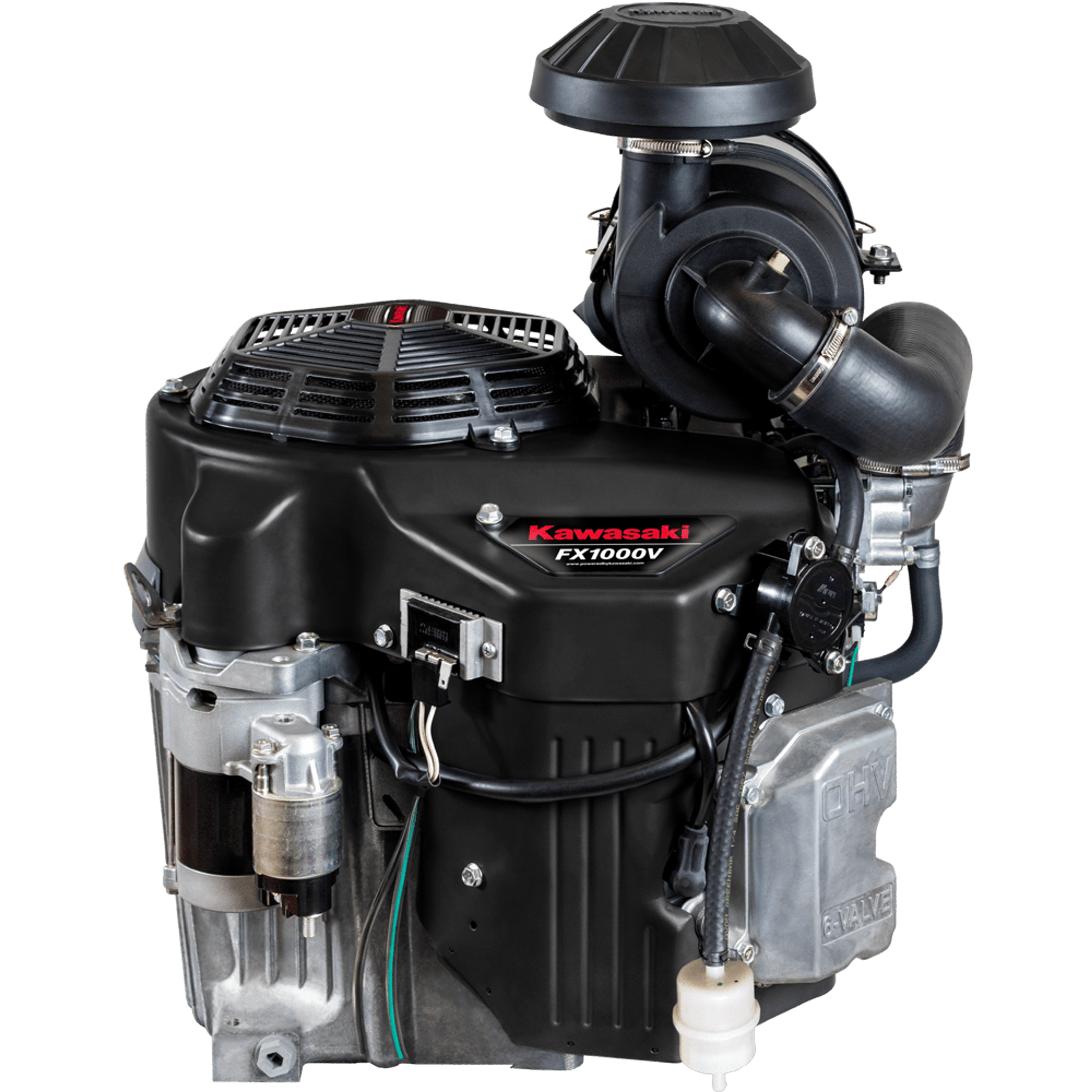
Specs
Displacement
Displacement
Engine displacement measures the overall physical size of the engine and its potential to perform work. A larger displacement means the engine can take in more air and fuel, which helps produce more power.
999 cc (61.0 cu. in.)
Number of Cylinders
Number of Cylinders
This is the number of combustion chambers inside the engine. More cylinders usually means smoother performance and greater power, while fewer cylinders normally communicates better fuel efficiency.
2
Bore x Stroke
Bore x Stroke
Bore is the width of each cylinder, and stroke is how far the piston moves inside it. The bore-and-stroke relationship affects how the engine makes power, influencing performance and fuel efficiency.
3.5 x 3.15 in. (89.15 x 80mm)
Compression Ratio
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio shows how much the engine squeezes the air-fuel mixture before ignition. Higher compression often leads to better performance and improved engine efficiency.
8.4:1
Oil Capacity w/filter
Oil Capacity w/filter
This is the total amount of oil the engine needs during an oil change when a new oil filter is installed. The filter holds extra oil, so the capacity is slightly higher than filling the engine alone.
2.0 U.S. qt (1.9 liters)
Maximum Power
Maximum Power
Maximum power is the highest level of horsepower the engine can produce, reflecting its ability to handle demanding work and maintain strong performance at higher speeds.
35.0 hp (26.1 kW) at 3,600 RPM
Maximum Torque
Maximum Torque
Torque measures the twisting force the engine can deliver. Higher torque helps with quick acceleration and gives the engine extra strength for tough jobs like climbing hills or carrying heavy loads.
56.0 ft-lbs (75.9 N·m) at 2,600 RPM
Dry Weight
Dry Weight
This is the weight of the engine without oil, fuel, coolant, or accessories. It shows the base weight of the engine for comparison between different models.
138.0 lbs (62.6 kgs)